GeoWeave was present at a hackathon where consultants and experts explored the end-to-end process of using drones for precision weed management. The event, organized by ILVO and VITO remote sensing, highlighted the steps required to convert drone-captured field data into actionable weed control maps, known as task maps, which can then be used to guide agricultural machinery.
Step 1: Drone Flight & Data Capture
During the hackathon, the team focused on planning and executing a drone mission over an agricultural plot. We were explained how the drone sampling technique can limit costs. These flights can be done by small, high-resolution drones, to capture detailed images of the fields. Variables such as flying altitude, weather conditions, and the crop growth stage were considered to optimize data quality

Step 2: Image Processing & AI Analysis
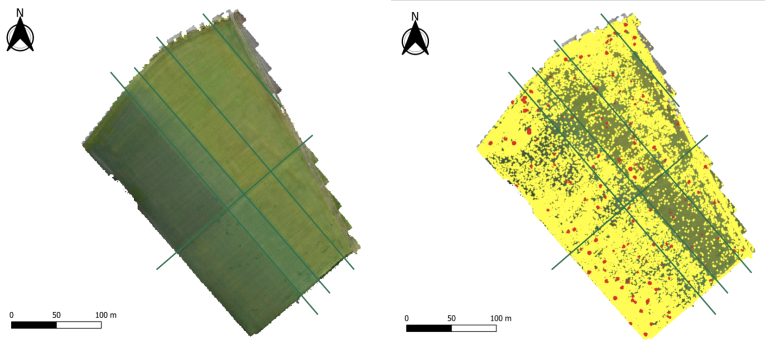
Step 3: Task Map Creation
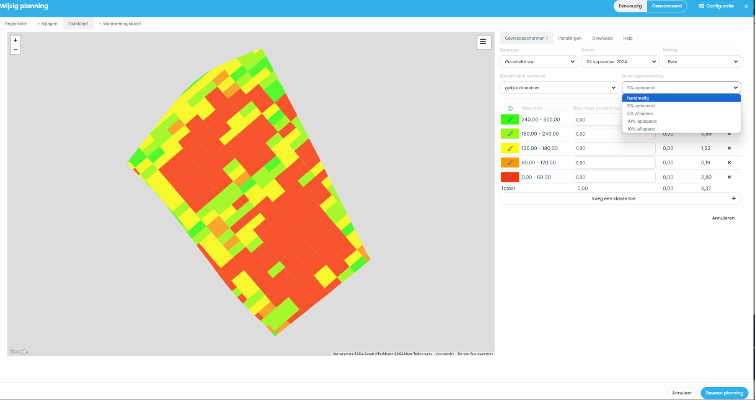
Step 4: Machine Application
The final step involved integrating the task maps into agricultural spraying machines. The data from the task maps were converted into formats such as ISO-XML, ensuring compatibility with modern agricultural machinery. Once uploaded, these machines automatically adjust their spray rates according to the map’s instructions, applying herbicides only where needed and avoiding areas that don’t require treatment.

Lessons from the Hackathon
GeoWeave provides environmental and agricultural GIS solutions by combining geospatial data with digital expertise and business intelligence. We seamlessly integrate existing data components from our partners to create clear, cohesive solutions.
Get in touch to discuss more.




